Difference between revisions of "SPEI(eng)"
From MyDewetra World
(Created page with " [Home] - [Observations] <br/> {| class="wikitable" |- |style="background-color: orange;" |Layer name |style="background-color: orange;"|St...") |
(No difference)
|
Revision as of 14:18, 16 November 2018
| Layer name | Standardized Precipitation-Evapotranspiration Index | |
| Tag | Drought | |
| Folder | ||
| Source | Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas | |
| Description | The SPEI fulfils the requirements of a drought index since its multi-scalar character enables it to be used by different scientific disciplines to detect, monitor and analyze droughts. Like the sc-PDSI and the SPI, the SPEI can measure drought severity according to its intensity and duration, and can identify the onset and end of drought episodes. The SPEI allows comparison of drought severity through time and space, since it can be calculated over a wide range of climates, as can the SPI. Moreover, Keyantash and Dracup (2002) indicated that drought indices must be statistically robust and easily calculated, and have a clear and comprehensible calculation procedure. All these requirements are met by the SPEI. However, a crucial advantage of the SPEI over other widely used drought indices that consider the effect of PET on drought severity is that its multi-scalar characteristics enable identification of different drought types and impacts in the context of global warming. More info at: SPEI documentation on line | |
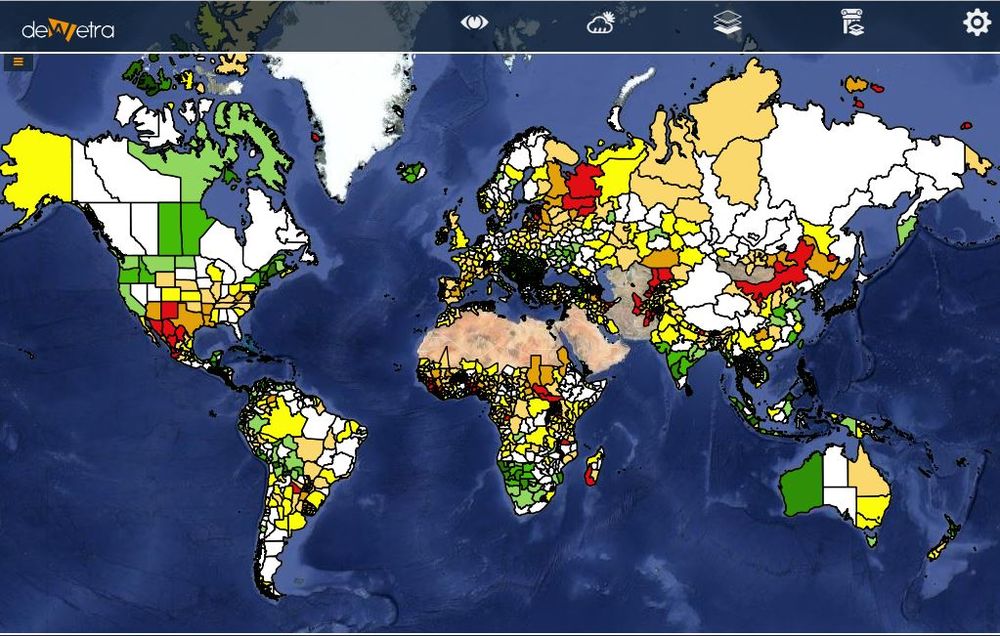
| Screenshot | ||
| Properties | ||
| Available variables | Standardized Precipitation-Evapotranspiration Index | |
| Available accumulations | Averaged on 3, 6, 9 and 12 months | |
| Available interpolation algorithms | ||
| Available filters | ||
| Spatial aggregations |