Difference between revisions of "Exclusion Mask"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[GFMS | [Home]]] - [[PRODUCTS | [back to | + | [[File:example7.jpg|right|100px|caption]] |
| + | [[GFMS | [Home]]] - [[PRODUCTS | [back to GFM Products]]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 10: | Line 11: | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | For its generation, we implement the methods proposed in section 1, following the identified problems of SAR-based flood mapping. <br> | + | For its generation, we implement the methods proposed '''in section 1''', following the identified problems of SAR-based flood mapping. <br> |
The parameter database stores for all locations on pixel basis the areas excluded by the four effect groups, with the radar shadow layer per local Sentinel-1 orbit configurations (up to six per location). During NRT operation, the relative orbit is determined from the S-1 metadata, and the respective Exclusion Mask layers are subset to the extent of the processed Sentinel-1 scene and form a single binary mask for exclusion areas. The Exclusion Mask layer values are described below. | The parameter database stores for all locations on pixel basis the areas excluded by the four effect groups, with the radar shadow layer per local Sentinel-1 orbit configurations (up to six per location). During NRT operation, the relative orbit is determined from the S-1 metadata, and the respective Exclusion Mask layers are subset to the extent of the processed Sentinel-1 scene and form a single binary mask for exclusion areas. The Exclusion Mask layer values are described below. | ||
| − | [[File:figure5.jpg]] | + | [[File:figure5.jpg|centre|border]] |
| Line 22: | Line 23: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| − | [[GFMS | [Home]]] - [[PRODUCTS | [back to | + | [[GFMS | [Home]]] - [[PRODUCTS | [back to GFM Products]]] |
Latest revision as of 13:09, 15 March 2021
[Home] - [back to GFM Products]
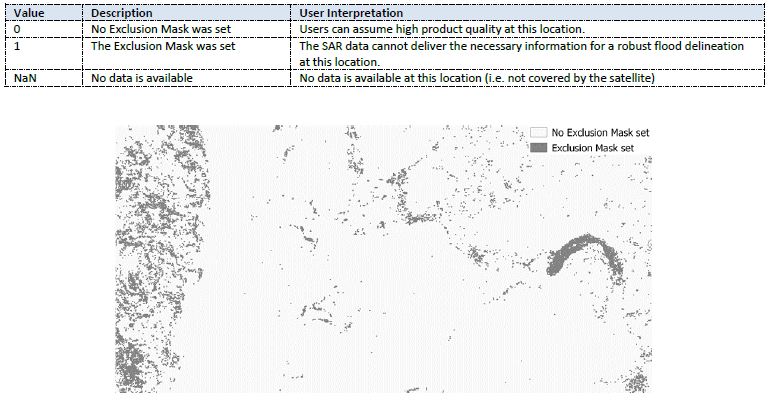
The Exclusion Mask indicates the pixel locations where the SAR data could not deliver the necessary information for a robust flood delineation. It combines static effects leading to
- no-sensitivity in flood mapping
- water-look-alikes
- strong topography
- radar shadows
For its generation, we implement the methods proposed in section 1, following the identified problems of SAR-based flood mapping.
The parameter database stores for all locations on pixel basis the areas excluded by the four effect groups, with the radar shadow layer per local Sentinel-1 orbit configurations (up to six per location). During NRT operation, the relative orbit is determined from the S-1 metadata, and the respective Exclusion Mask layers are subset to the extent of the processed Sentinel-1 scene and form a single binary mask for exclusion areas. The Exclusion Mask layer values are described below.
Note
As no-sensitivity is a problem leading often to an underestimation of floods rather than to overestimation (e.g. in urban areas), the no-sensitivity -masking is only applied to pixels that are classified as non-flooded, whereas pixels classified as flooded are kept un-masked. Any no-data areas from the flood algorithm are forwarded to this layer and added as no-data values.